Heating networks are one of the most efficient ways to provide heat to a home. But that one must be supplied with energy and are, most often, by carbon-based processes. The use of thermodynamic machines such as ORCs or heat pumps makes it possible to supply these networks with heat efficiently and continuously

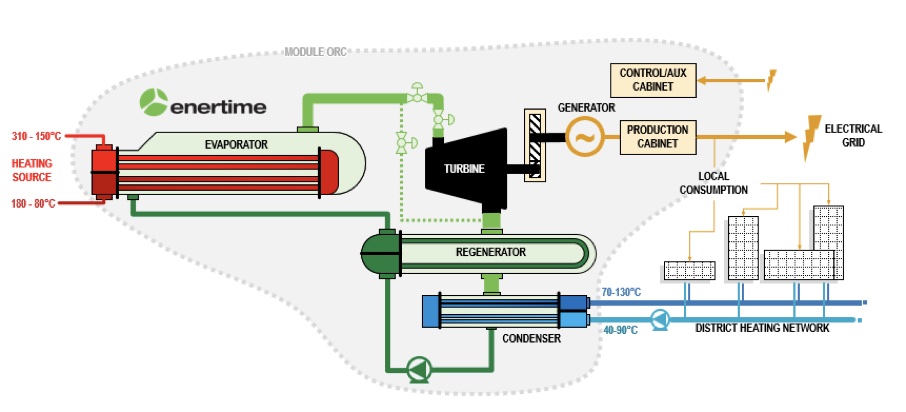
ORC, AN HYBRID SOLUTION FOR HEAT AND ELECTRICITY PRODUCTION
Thanks to their great flexibility in terms of temperature of design, ORCs are an intelligent and carbon-free solution for transforming energy, whether in thermal, electrical or both forms. Since thermoelectric conversion is in the best case at 25% efficiency, the rest of the heat must be dissipated in a nearby environment at a lower energy level.
The heat sources can be diverse : incinerators, biomass power plant, heavy industries…
Thanks to an hydrocondenser, the machine will be cooled by the network’s water and by energy transfer this water will be heated and returned to the network at a higher temperature. The temperature of the water leaving the condenser is a technological parameter, flexible and adjustable even once the machine has been put into service.
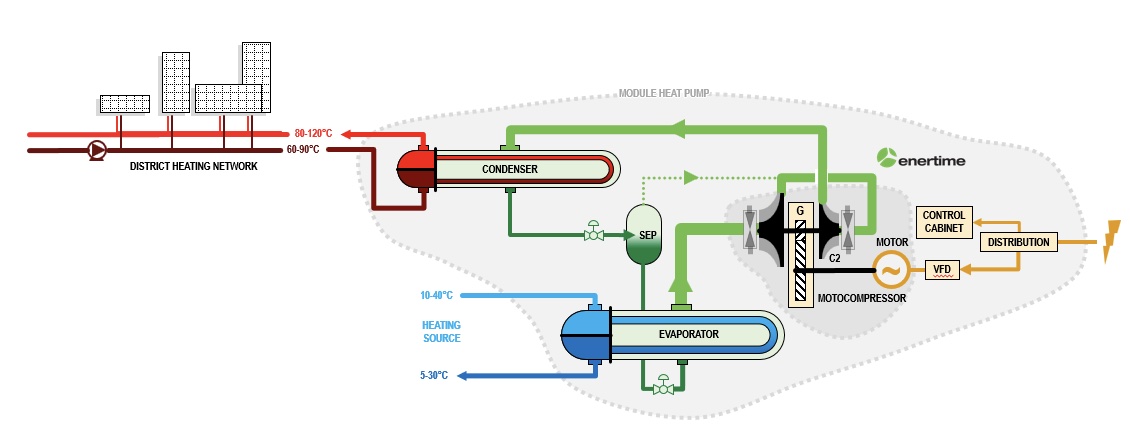
THE HEAT PUMP, PRODUCTION OF HEAT AND COLD
The industry justifies of a large quantity of effluents at low temperatures in liquid form (water, condensates) that can be recovered.
The heat pump is, by definition, a machine making it possible to transport heat from point A to point B and which, by injection of a mechanical power supply, sees its temperature increase. Supplying waste heat to district heating networks is therefore one of the main applications of the heat pump.
Reciprocal, a production of heat leads to a production of cold. The city of future includes cooling networks, called-chilled water networks, which are necessary for cooling urban areas and industrial processes.